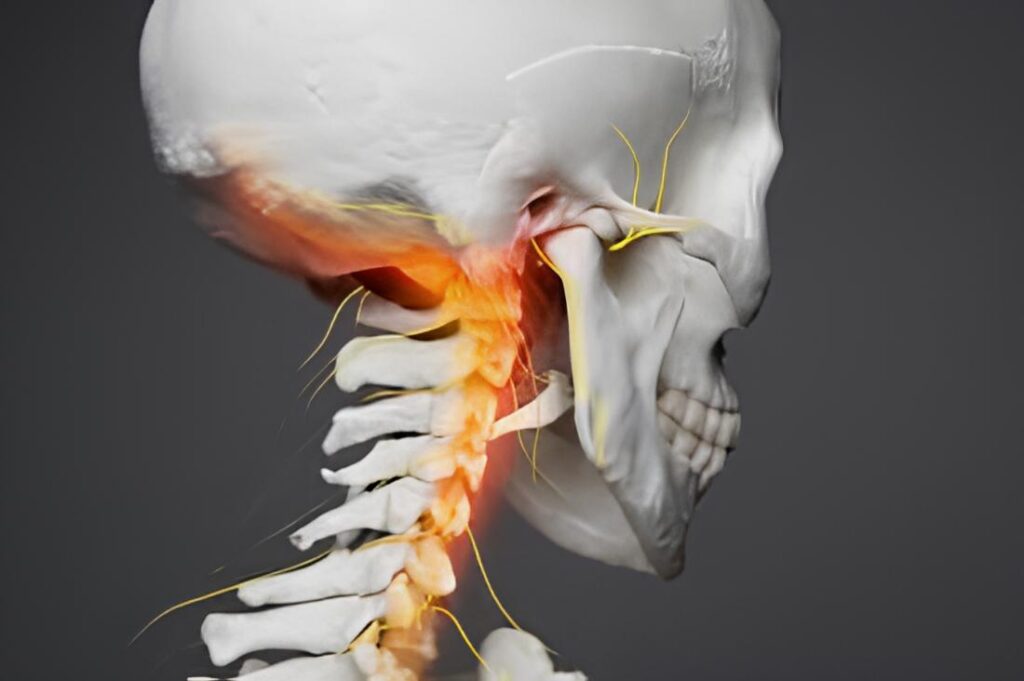
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI) occurs when blood flow to the back of the brain is reduced or blocked. This region controls essential functions like balance and movement.
While many people with VBI experience only mild symptoms, the condition significantly increases the risk of stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA or mini-stroke). In severe cases, it can cause permanent disability or death.
Treatment typically involves lifestyle changes and medications. Surgery may be necessary if symptoms persist.
Causes:
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
- Arterial dissection
- Vertebral artery compression (e.g., from neck movement)
- Blood clots
- Vasculitis
Symptoms
VBI symptoms vary and may include:
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Confusion or delirium
- Swallowing difficulties
- Poor coordination (ataxia)
- Double or blurred vision
- Fainting (syncope)
- Sudden loss of balance (drop attacks)
- Numbness or weakness
- Slurred speech
- Nausea and vomiting
- Urinary incontinence.
Types
A rare form, transient vertebrobasilar insufficiency, happens when turning or rotating the head reduces blood flow. It is also known as:
- Bow hunter syndrome
- Rotational vertebrobasilar insufficiency
- Head-turning syncope
Risk factor
VBI is more common in people over 50 and those with:
- Coronary artery or peripheral artery disease
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
- Diabetes or obesity
- A history of smoking
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
- Hyperlipidemia (high fat levels in the blood)
- Cardiac conditions such as atrial fibrillation or blood clotting disorders
- Vertebral artery dissection
Diagnosis
- Imaging: CT or MRI scans of the brain and blood vessels
- Angiography: X-ray images of arteries
- CTA/MRA: 3D imaging of blood vessels
- Echocardiogram: Ultrasound of the heart
- ECG/Holter monitor: Monitors heart rhythms
- Blood tests: PT and PTT to assess clotting
Physiotherapy management
Physiotherapy plays a supportive and rehabilitative role in the management of Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency (VBI), especially after acute medical management has stabilized the patient. The goal is to improve balance, reduce dizziness, enhance mobility, and prevent falls, while avoiding movements that could worsen blood flow.
Physiotherapy Goals in VBI:
- Improve balance and postural stability
- Reduce dizziness and vertigo (if present)
- Restore functional mobility
- Prevent falls
- Educate on safe movement patterns, especially of the neck
Key Physiotherapy Interventions:
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT):
For patients experiencing dizziness or vertigo:
- Gaze stabilization exercises (e.g., VOR x1 and VOR x2 exercises)
- Habituation exercises (to reduce sensitivity to motion)
- Balance training on firm and unstable surfaces
Balance and Coordination Training:
- Tandem walking
- Single-leg stance
- Use of balance boards or foam surfaces
- Dynamic gait activities
Gait Training:
- Walking with visual cues
- Use of assistive devices (e.g., cane or walker if needed)
- Treadmill walking under supervision
Cervical Spine Care:
Because head and neck movements can affect vertebral artery blood flow:
- Avoid excessive cervical extension and rotation, especially early on
- Gentle neck ROM (range of motion) exercises, if tolerated
- Postural correction exercises (e.g., chin tucks, scapular retraction)
Cardiovascular Conditioning:
Low-impact aerobic activity (walking, stationary cycling) to:
- Improve general circulation
- Build endurance
- Enhance vascular health
Patient Education:
- Safe turning techniques for the head/neck
- Fall prevention strategies
- Importance of compliance with medications and vascular risk management
What are common symptoms of Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency (VBI)?
Common symptoms include dizziness, confusion, double vision, slurred speech, poor coordination, and sudden loss of balance.
What is the role of physiotherapy in managing VBI?
Physiotherapy helps improve balance, reduce dizziness, restore mobility, and prevent falls, while teaching safe neck movements to avoid worsening symptoms.
What are the main risk factors for developing VBI?
Risk factors include being over 50, having high blood pressure, diabetes, atherosclerosis, a history of smoking, and cardiac conditions like atrial fibrillation.