Definition of Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder(ADHD)
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder(ADHD) one of the most common mental disorders, affecting 5–8% of children, primarily boys, and often continuing into adulthood. It impacts learning and daily functioning, characterized by three main features:
Inattention – Difficulty staying focused.
Hyperactivity – Excessive movement, fidgeting, or talking.
Impulsivity – Acting without thinking, often leading to risky behavior.
Symptoms
A D H D symptoms vary in intensity and differ between children and adults.
Inattention: Difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, trouble following instructions, and poor organization.
Hyperactivity: Excessive talking, restlessness, constant movement, and difficulty staying seated.
Impulsivity: Interrupting others, difficulty waiting for turns, and making impulsive decisions.
Causes
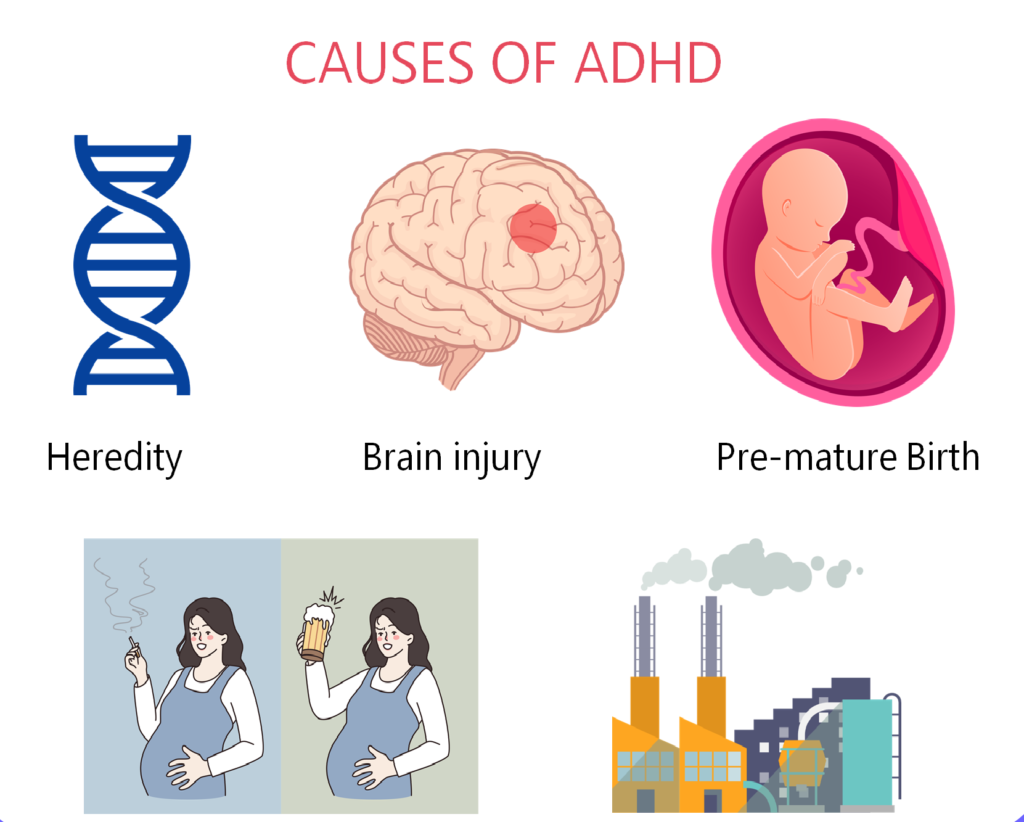
The exact cause of A D H D is not fully understood, but several factors contribute:
1. Genetics: A D H D runs in families, with multiple genes involved.
2. Brain Structure & Function: Lower activity in brain regions responsible for attention and self-control, along with reduced brain volume in key areas.
3. Prenatal & Birth Factors: Exposure to tobacco, alcohol, or drugs during pregnancy, premature birth, and low birth weight increase the risk.
4. Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins like lead, extreme stress during pregnancy, and social conditions such as poverty.
5. Diet & Lifestyle: While not a direct cause, poor nutrition, lack of sleep, and inactivity may worsen symptoms.
A D H D likely results from a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental influences, manifesting uniquely in each person.
Therapies for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder(ADHD)

Treatment typically involves a combination of strategies based on individual needs:
Behavioral Therapy: Reinforces positive behaviors and reduces problematic ones.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy : Helps manage emotions, impulsivity, and self-regulation.
Parent Training & Family Therapy: Equips families with strategies to support children effectively.
Social Skills Training: Teaches communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
Educational Support: Classroom accommodations and learning strategies to aid academic success.
A comprehensive approach combining therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes medication can help individuals manage A D H D effectively.A D H D affects focus, behavior, and impulse control. It stems from genetic, neurological, and environmental factors and is managed with therapy.
1. Q:What are the three main features of A D H D?
A:Inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
2. Q: What factors contribute to the development of A D H D?
A: Genetics, brain structure, prenatal and birth factors, environmental influences, and lifestyle.
3. Q:What are common therapies for managing A D H D?
A: Behavioral therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (C B T), parent training, social skills training, and educational support.

