How to Recognize lacking of Protein in your body?
Protein, a crucial macronutrient composed of amino acids, plays a vital role in the body, often referred to as the foundational blocks for muscles. Beyond muscle repair and maintenance, proteins provide energy, regulate hormones, and act as enzymes that facilitate chemical reactions. They also help regulate the transport of substances across cell membranes and bolster the immune system against diseases.
The recommended dietary allowance to prevent deficiency for an average sedentary adult is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, individuals should consider increasing their protein intake under medical guidance if they experience any of the following symptoms.
Weakness, Muscle Loss, and Fatigue
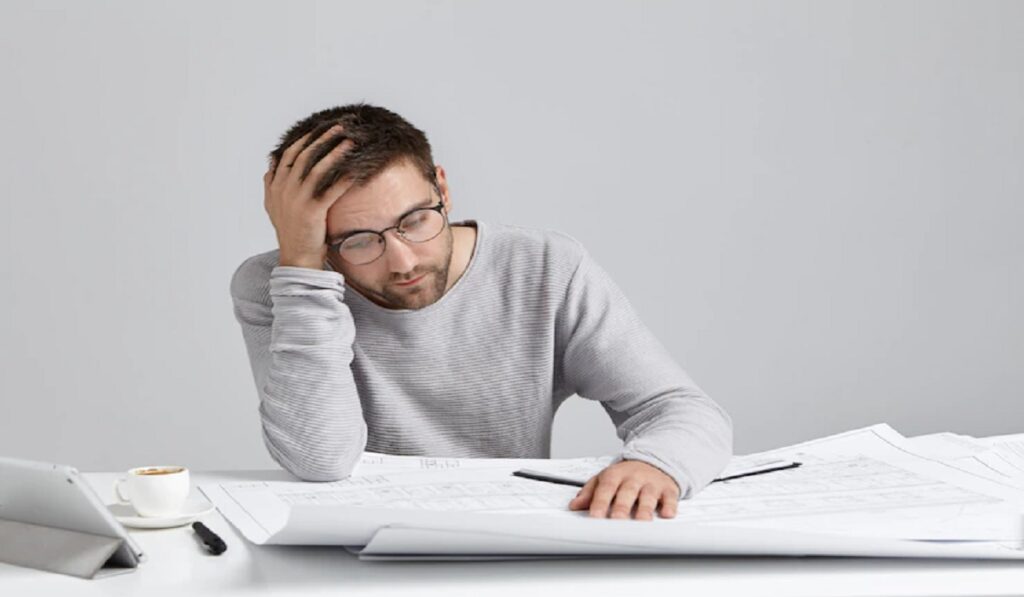

Lacking of protein can lead to weakness, fatigue, and muscle loss. When dietary protein is inadequate, the body compensates by breaking down skeletal muscle to meet its protein needs. This process, over time, results in muscle wasting, reducing strength and slowing metabolism. Consequently, individuals may experience increased weakness and fatigue.
Slow-Healing Injuries

Lacking of protein in the body can significantly slow down the healing process following an injury from an accident, intense workout, or surgery. Protein is essential for building new cells and tissues, crucial for wound repair and recovery. Without adequate protein, the regeneration of new cells can be delayed, prolonging the healing of wounds and injuries.
Increased Appetite

Constant feelings of hunger, persistent food cravings, or frequent binge-eating on snacks may indicate a protein deficiency. Protein is known for its high satiety factor, helping to keep you feeling full for extended periods. When protein intake is inadequate, you may experience stronger hunger pangs and cravings.
Reduced Immune Function
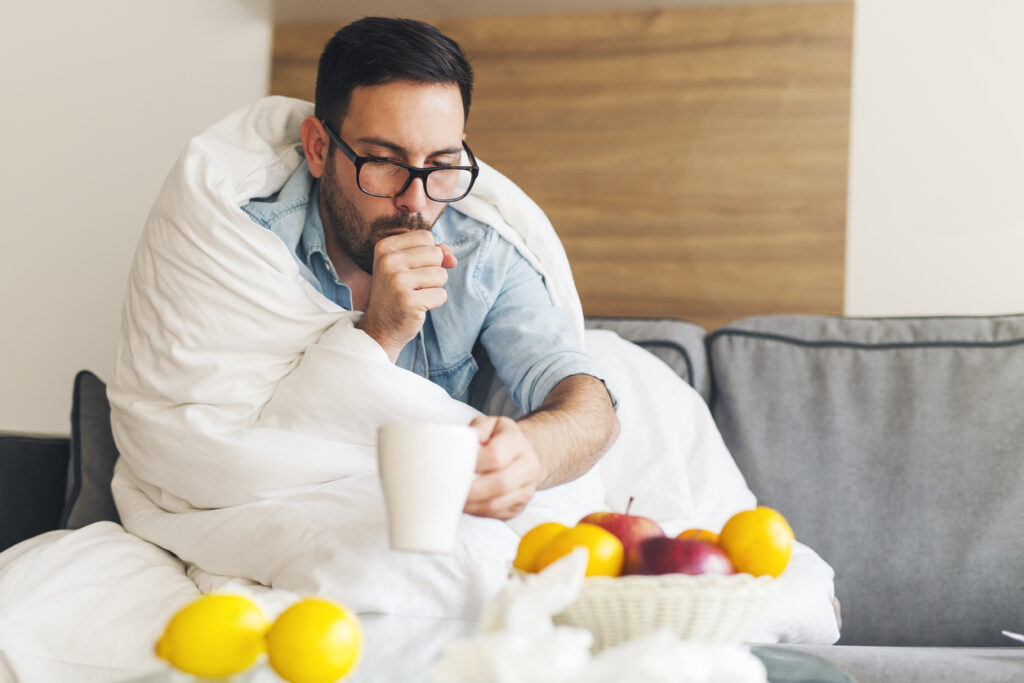

Insufficient protein intake can compromise your immune system, making you more susceptible to sickness. Protein plays a crucial role in supporting immune function and providing the necessary amino acids for building immune cells. Ensuring an adequate protein intake can help strengthen your immune system, enhancing its ability to fend off viruses and bacteria effectively.
Issues with Hair, Nails, and Skin
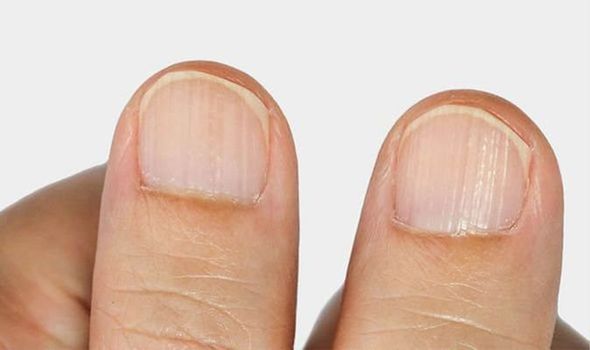
Early signs of low protein levels in the body can manifest as weak, brittle nails, dry skin, and thinning hair. These symptoms occur because proteins like elastin, collagen, and keratin are essential for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. Inadequate protein intake or deficiency can impair the formation and strength of these tissues, leading to noticeable changes in appearance and texture.
How does protein deficiency affect muscle strength?
Insufficient protein intake can lead to muscle loss, weakness, and fatigue as the body breaks down muscle tissue to compensate for the deficiency.
Why does protein deficiency slow down injury recovery?
Protein is essential for cell and tissue repair. Without enough protein, the healing process is delayed, prolonging wound recovery.
How can low protein intake impact immune function?
A protein deficiency weakens the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.

