Introduction:
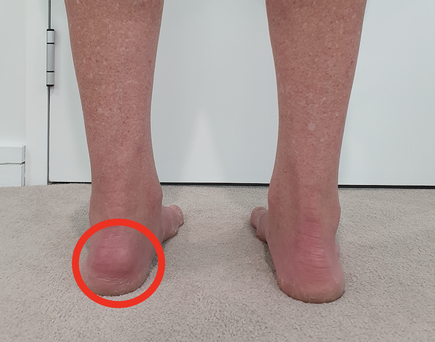
Haglund’s Syndrome, often referred to as “pump bump”, is a common condition significant posterior heel pain. It is associated with retrocalcaneal bursitis.It affects individuals across various activity levels, from athletes to those with sedentary lifestyles.
Definition:
Haglund’s Syndrome is a musculoskeletal condition characterized by a bony enlargement on the posterior heel bones (calcaneus) at the insertion of the Achilles tendon. This bony prominence irritates the associated soft tissues, including the retrocalcaneal bursa and the Achilles tendon, leading to a pain and swelling.
Etiology:
The exact cause of Haglund’s Syndrome is multifunctional, often involving a combination of anatomical predisposition and external factors:
- Foot biomechanics: With Pes cavus( high arches) the heel is tilted backward into the Achillis Tendon . Therefore a bony protrusion develops due to the constant irritation of the back of the heel bone as it rubs against the tendon.
- Improper Footwear: stiff- backed shoes, heard surface shoes especially those with rigid heel counters, can rub against the heel, exacerbating irritation.
- Tight Achilles tendon: Pain is caused by compressing the tender and the inflamed bursa.
- Genetics: A family history of similar bony prominences might indicate a genetic predisposition.
Clinical Feature:
Patient typically present with:
- Visible bump or an enlarged bony prominence on the back of the heel, especially during or after activity.
- Heel pain spicily when the foot is bends upwards, stretching the Achilles tendon.
- Swelling and inflammation in the Achilles tendon.
- Severely mobility. The friction between the soft tissue at the back of the heel and the shoe. Symptoms are aggravated by wearing footwear with hard heel edges, as this impinge on the bursa and the Achilles tendon on the calcaneas.
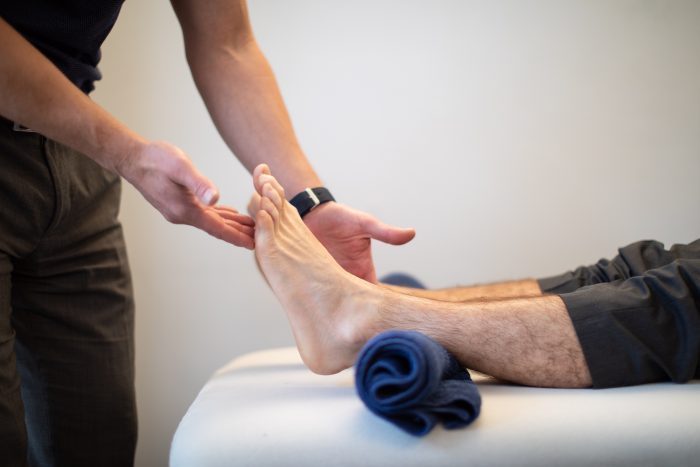
Physiotherapy Management:
Conservative management, particularly physiotherapy , is the cornerstone of treatment:
Management of Inflammation and pain:
Ice, immobilization,ultrasound and activity modification.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercise:
- Lower leg strengthening exercises are vital.
- Achilles stretches (contra-indicated if Achilles was injured or if it was detached and re-attached intra-operatively)
Manual Therapy:
Soft tissue mobilization and massage techniques to address muscle imbalances and facial restrictions.
Footwear Modification:
Advising on appropriate footwear with open backs or silicon gel heel pad counters to reduce pressure.
Orthotics:
Custom or off- the – shelf orthotics to correct foot biomechanics and reduce pressure on the heel.
Patient Education:
Guidance on proper activity modification, warm-up and cool- down routines.
Diet and Nutrition Support (Important for Recovery):
Diet plays a supportive role in reducing inflammation and promoting tissue healing in Haglund’s Syndrome.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporate omega-3-rich foods such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Vitamin C & Collagen: Promote tendon repair through citrus fruits, berries, and collagen supplements.
- Calcium & Vitamin D: Strengthen bones with milk, leafy greens, and moderate sunlight exposure.
- Hydration: Proper fluid intake prevents tissue stiffness and aids recovery.
Conclusion:
Hugland’s deformity is a bony protrusion on the posterolateral part of the heel. It occurs mostly in young females. Understanding this condition is for timely diagnosis and effective management. A comprehensive treatment plan and Early diagnosis can significantly alleviate recurrence, allowing individuals to return to their desired activity levels without persistent heel pain.
Q1. What is Haglund’s Syndrome?
A1. Haglund’s Syndrome is a bony enlargement on the back of the heel that irritates the Achilles tendon and bursa, causing pain and swelling.
Q2. What are common causes of Haglund’s Syndrome?
A2. It is caused by high arches, tight Achilles tendon, improper footwear, and genetic factors.
Q3. How does physiotherapy help in Haglund’s Syndrome?
A3. Physiotherapy reduces pain and inflammation using ice, stretching, strengthening, manual therapy, and footwear modification.