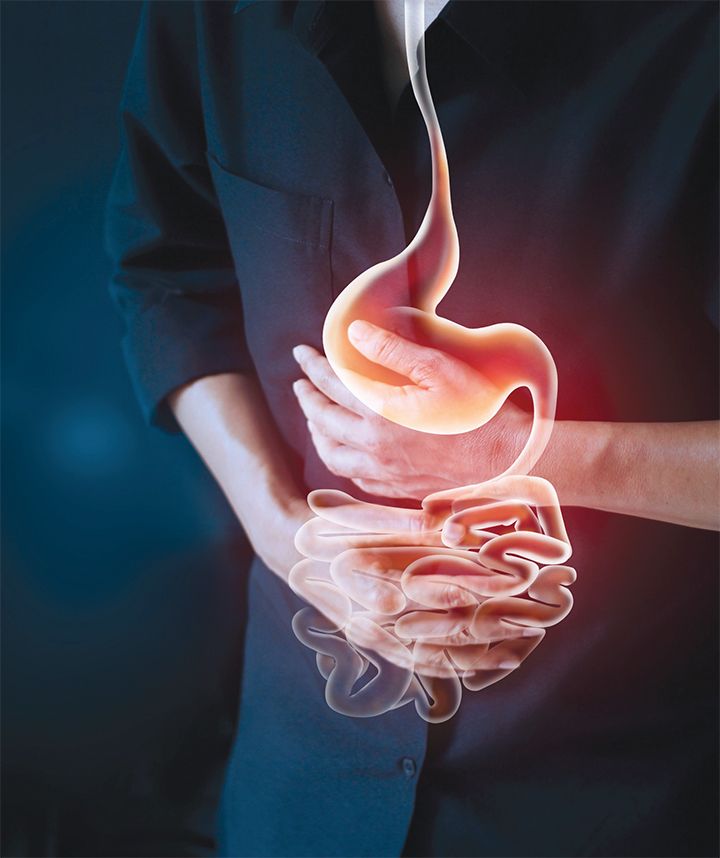
Foods That Could Be Making Your IBS Worse
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder characterised by symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, and constipation. While triggers vary from person to person, certain foods are known to commonly aggravate IBS symptoms. These foods would triggers your symptoms – 1. Dairy Products Milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy items can be problematic, …