Introduction
A concussion is a common form of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) caused by a sudden impact or force to the head or body. It temporarily disrupts normal brain function and can affect physical, cognitive, and emotional health. Early recognition and appropriate rehabilitation are essential for safe recovery and prevention of long-term complications.
Definition
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury resulting from a direct or indirect force to the head, leading to transient neurological dysfunction without structural brain damage visible on routine imaging.
Etiology
A concussion commonly occurs due to:
- Sports-related injuries (football, boxing, hockey, cricket)
- Road traffic accidents
- Falls, especially in children and older adults
- Assaults or physical violence
- Workplace or recreational accidents
The injury results from rapid acceleration-deceleration or rotational forces acting on the brain.
Clinical Features
Clinical features vary in severity and duration and may appear immediately or develop hours later:
- Temporary loss of consciousness
- Slow reaction time
- Altered mental status or confusion
- Trouble concentrating
- Sensitivity to light or noise
Complications
If not managed properly, a concussion may lead to:
- Post-concussion syndrome
- Persistent headaches and dizziness
- Emotional disturbances such as anxiety or depression
- Cognitive and memory deficits
- Increased risk of repeated concussions
Risk Factors
- Participation in contact sports
- Previous history of concussion
- Poor protective equipment use
- Alcohol or substance use
- High-risk occupations
- Young age and elderly population
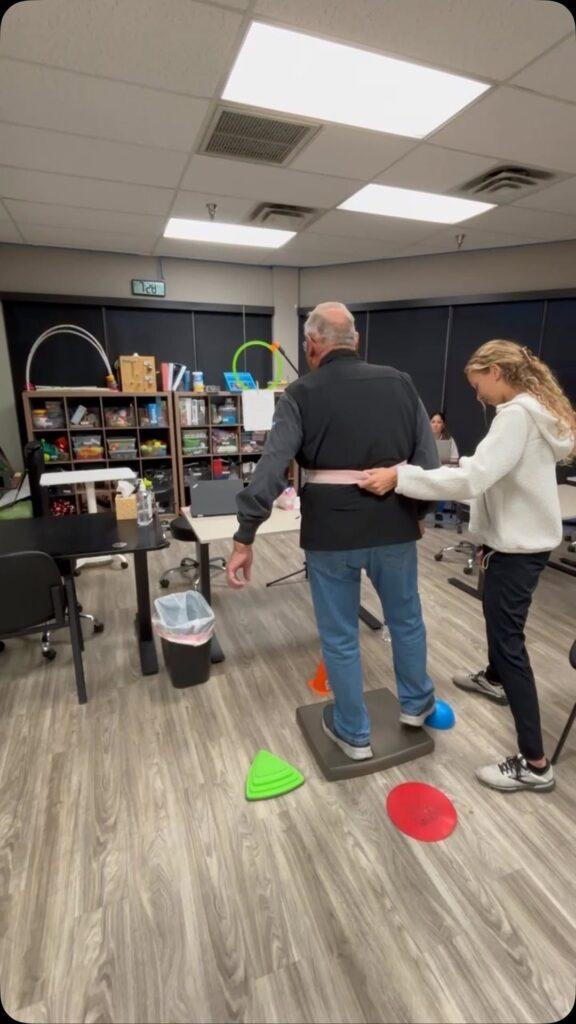

Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in concussion rehabilitation, especially for persistent symptoms:
Key physiotherapy interventions include:
- Gradual return-to-activity programs
- Vestibular rehabilitation for dizziness and balance issues
- Postural correction and mobility exercises
- Cervical spine assessment and treatment
- Gait and balance training
- Aerobic conditioning under symptom-limited thresholds
- Education on symptom monitoring and activity pacing
Rehabilitation programs are individualized and follow a stepwise, symptom-guided approach to ensure safe recovery.
Conclusion
A concussion is a mild but potentially serious brain injury that requires timely diagnosis and structured management. A multidisciplinary approach, including physiotherapy, is essential for symptom resolution, safe return to activity, and prevention of long-term complications. Early rehabilitation remarkably improves functional recovery and quality of life.
Q1. What is a concussion?
Ans: A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury caused by a sudden impact, leading to temporary disruption of brain function.
Q2. What are the common clinical features of a concussion?
Ans: Confusion, slow reaction time, difficulty concentrating, sensitivity to light or noise, and temporary loss of consciousness.
Q3. How does physiotherapy help in concussion recovery?
Ans: Physiotherapy aids recovery through vestibular rehabilitation, graded activity progression, balance training, and symptom-guided exercises.