Introduction
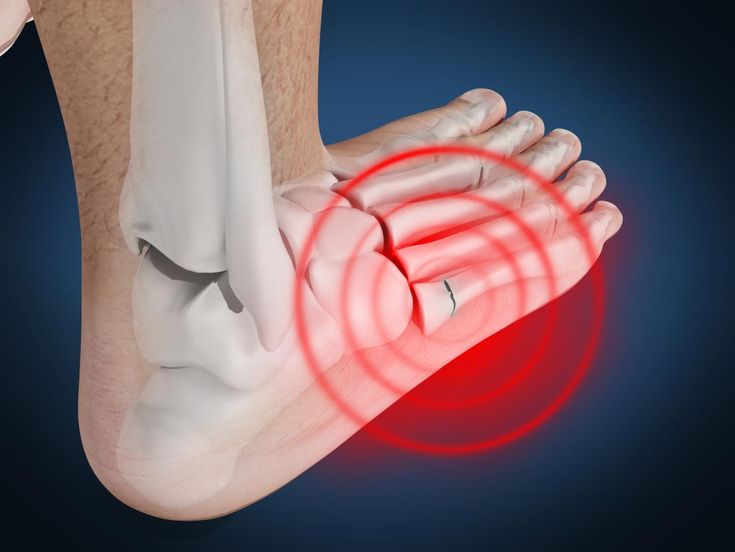
Fracture of the Metatarsal refers to a break in one or more of the five long bones of the foot located between the tarsal bones and toes. Metatarsal fractures are common foot injuries seen in athletes, dancers, and individuals exposed to trauma. If untreated, they can significantly impair walking and weight-bearing activities.
Etiology
Metatarsal fractures may occur due to various causes, including:
- Direct trauma to the foot, such as heavy object impact
- Falls from height or road traffic accidents
- Twisting injuries or a sudden change in direction
- Overuse or repetitive stress, leading to stress fractures
- Osteoporosis or weakened bones in elderly individuals
- Sports activities like running, football, or dancing
Clinical Features
Common signs and symptoms of metatarsal fractures include:
- Localized pain in the midfoot or forefoot
- Swelling and redness over the affected area
- Tenderness on palpation
- Pain aggravated by standing or walking
- Difficulty in weight bearing
- In some cases, visible deformity or abnormal alignment of toes
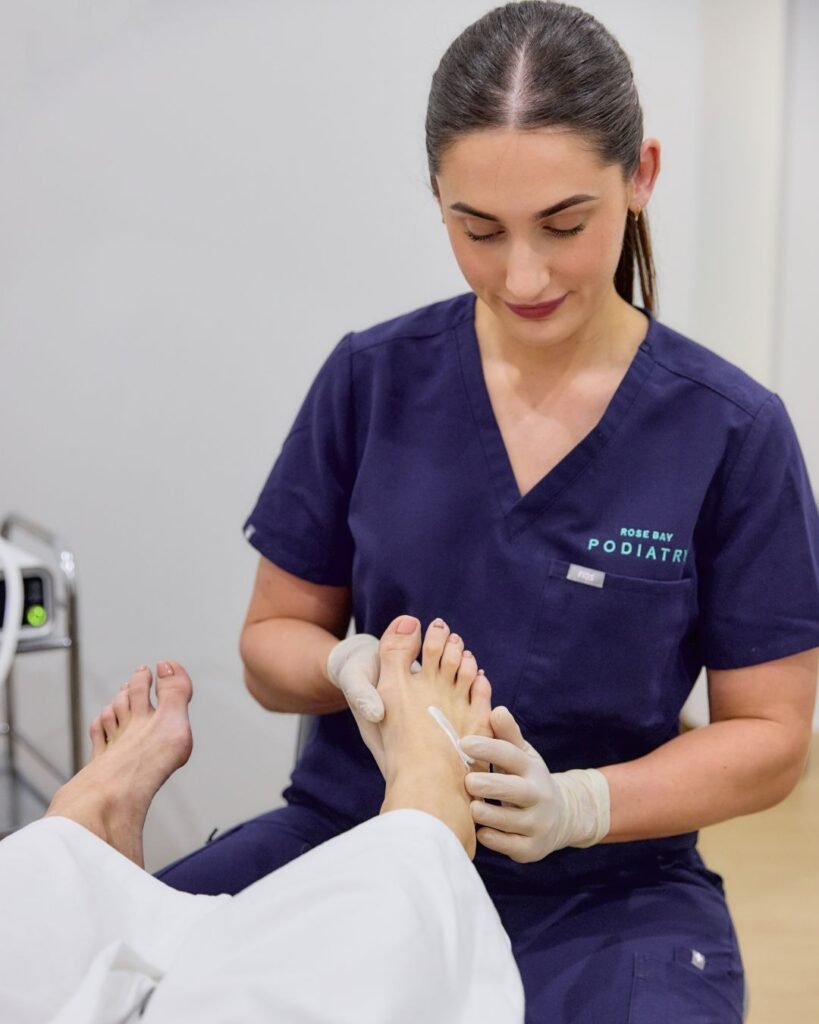
Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in restoring foot function after a metatarsal fracture.
- Immobilization Phase:
Pain and swelling control using elevation, ice therapy, and gentle toe movements if permitted. Non–weight-bearing mobility training is initiated. - Strengthening Phase:
Exercises for intrinsic foot muscles, calf strengthening, and resistance training improve stability and strength. - Post-Immobilization Phase:
Gradual weight-bearing exercises are introduced. Active range of motion exercises for the ankle and toes help restore mobility. - Functional Training:
Balance training, gait re-education, and proprioceptive exercises help in a safe return to daily activities and sports.
Complications
If not managed properly, metatarsal fractures can lead to:
- Delayed union or non-union
- Chronic foot pain
- Reduced foot strength and endurance
- Malunion causing altered foot biomechanics
- Increased risk of re-injury
Conclusion
Fracture of the Metatarsal is a common yet potentially disabling foot injury. Early diagnosis, appropriate medical care, and structured physiotherapy are essential to ensure optimal healing, restore mobility, and prevent long-term complications.
Q1. What is a metatarsal fracture?
Answer: A metatarsal fracture is a break in one or more of the five long bones of the foot, often causing pain and difficulty in walking or weight bearing.
Q2. What are the common symptoms of a metatarsal fracture?
Answer: Common symptoms include localized foot pain, swelling, tenderness, redness, pain while walking, and difficulty in weight bearing.
Q3. How does physiotherapy help in metatarsal fracture recovery?
Answer: Physiotherapy reduces pain and swelling, restores foot strength and mobility, improves balance and gait, and helps prevent long-term complications.