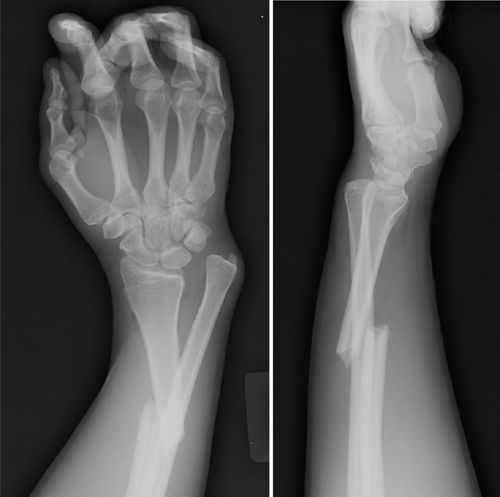
Definition
Galeazzi Fracture is defined as a fracture of the distal or middle third of the radius accompanied by dislocation or subluxation of the distal radioulnar joint. It is often referred to as a “fracture of necessity” because surgical management is usually required in adults.
Mechanism of Injury
- Fall on an outstretched hand with the forearm in pronation
- Sports injuries involving rotational forces
- Direct trauma to the forearm (road traffic accidents)
- High-energy impact injuries, especially in adults
- Industrial or occupational injuries involving heavy impact or torsional stress
In children, the injury may occur with lower energy and can sometimes be managed conservatively.
Clinical Features
- Severe pain in the forearm and wrist
- Visible deformity of the forearm
- Swelling and tenderness along the radius
- Painful or restricted wrist movement
- Limited forearm rotation (pronation and supination)
- Instability or prominence at the distal radioulnar joint
- In severe cases, associated nerve or vascular symptoms
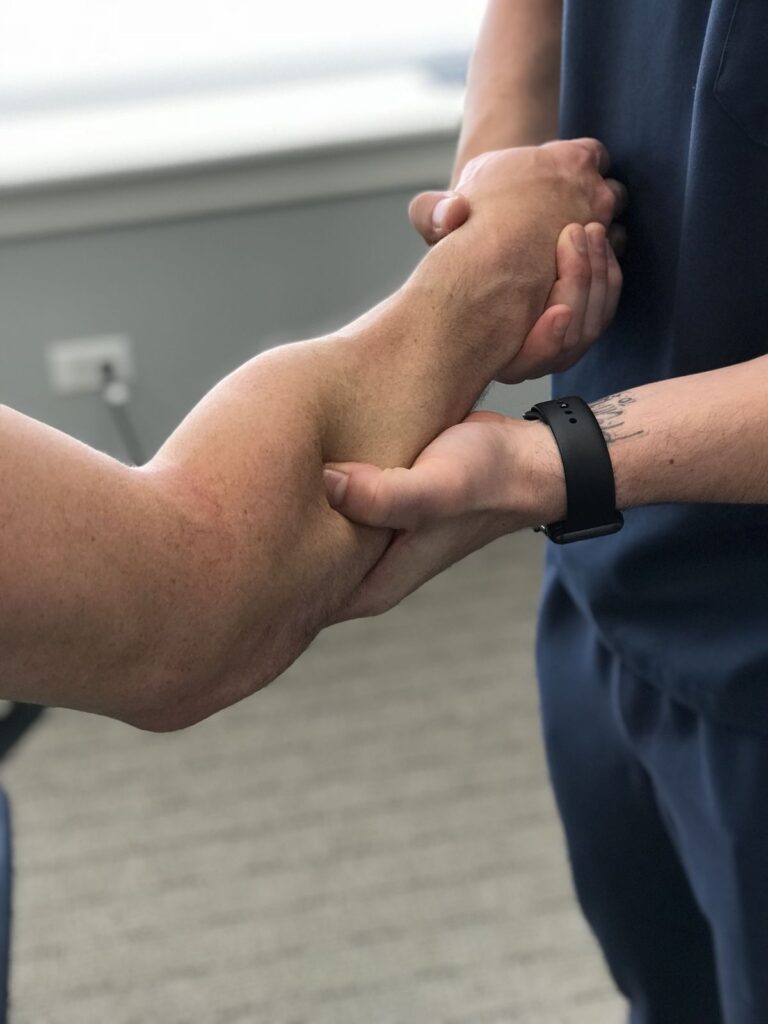
Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a vital role after surgical fixation or immobilization.
- During immobilization:
- Active range of motion (AROM) exercises for the shoulder, fingers, and thumb
- Isometric exercises for the elbow and forearm muscles
- Post-immobilization phase:
- Gradual restoration of elbow and wrist mobility
- Progressive forearm pronation and supination exercises
- Strengthening exercises for wrist flexors, extensors, and grip
- Functional training to restore daily activities
With proper rehabilitation, functional recovery is typically achieved within 8–12 weeks.
Complication
- Chronic instability of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ)
- Malunion or non-union of the radius
- Persistent wrist pain and deformity
- Restricted forearm pronation and supination
- Post-traumatic arthritis of the wrist
- Nerve injury (especially radial or ulnar nerve)
Conclusion
A Galeazzi Fracture is a complex forearm injury that can remarkably impair wrist and forearm function if not treated appropriately. Early surgical management combined with structured physiotherapy ensures joint stability, restores movement, and improves functional outcomes. Timely rehabilitation is key to achieving optimal recovery.
Q1. What is a Galeazzi fracture?
Answer: A Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal or middle third of the radius with dislocation or subluxation of the distal radioulnar joint.
Q2. What are the common clinical features of a Galeazzi fracture?
Answer: Severe forearm and wrist pain, swelling, visible deformity, restricted wrist movement, and limited forearm rotation with DRUJ instability.
Q3. How does physiotherapy help in Galeazzi fracture recovery?
Answer: Physiotherapy restores wrist and forearm mobility, improves strength and grip, and helps regain functional activities after immobilization or surgery.