Introduction
Hydrocephalus is a neurological condition characterized by abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain ventricles. This excessive fluid buildup increases intracranial pressure and can impair brain development and function. Early diagnosis, medical management, and physiotherapy play avital role in improving functional outcomes and quality of life.
Definition
Hydrocephalus is defined as a pathological condition in which there is an imbalance between the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to ventricular dilation and increased pressure on brain tissues.
Etiology
Hydrocephalus may be congenital or acquired and can occur at any age. Common causes include:
- Congenital brain malformations
- Intraventricular hemorrhage, especially in premature infants
- Brain tumors obstructing CSF flow
- Central nervous system infections, such as meningitis
- Traumatic brain injury
- Post-surgical complications
Clinical Features
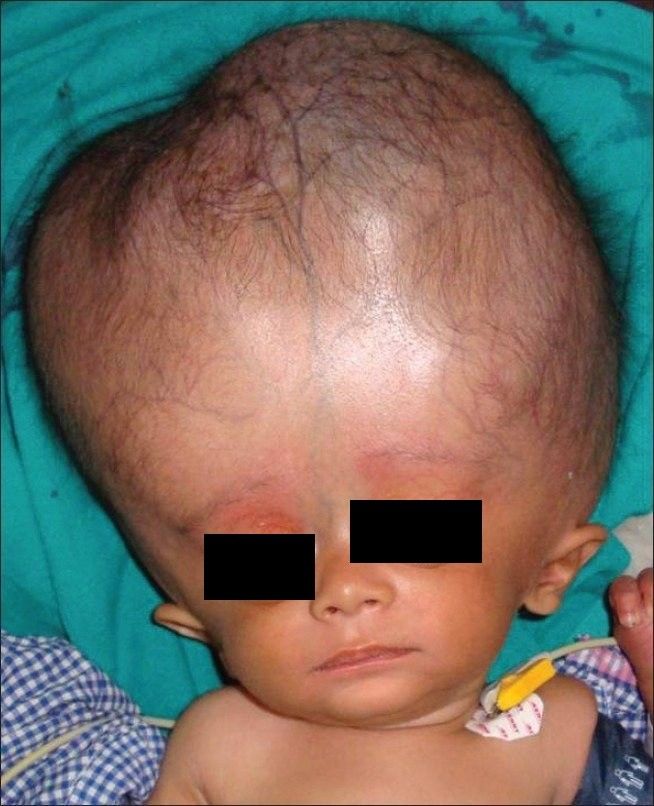
The clinical presentation of hydrocephalus varies depending on age, cause, and severity. Infants may show head enlargement, while older children and adults often present with neurological and functional impairments. Cognitive, motor, and balance disturbances are common.
Signs and Symptoms
- Enlarged head circumference
- Headache and vomiting
- Delayed developmental milestones
- Seizures
- Poor balance and coordination
- Gait disturbances
- Visual disturbances
- Memory and concentration difficulties
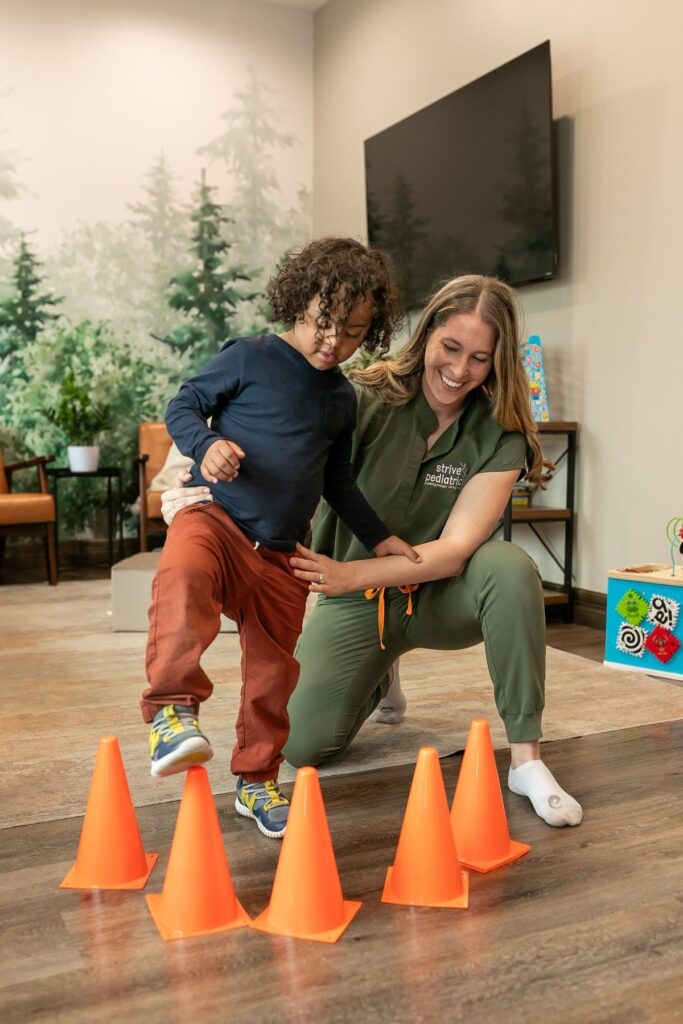

Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy focuses on improving mobility, strength, balance, and functional independence:
- Developmental stimulation in infants
- Postural control and head control exercises
- Balance and coordination training
- Gait training with or without assistive devices
- Strengthening of trunk and limb muscles
- Functional training for daily activities
- Prevention of contractures and deformities
- Family and caregiver education
Physiotherapy is particularly beneficial after surgical interventions such as ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement.
Complications
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Cognitive impairment
- Motor delays and weakness
- Visual and hearing deficits
- Shunt malfunction or infection
- Learning difficulties
- Decreased quality of life if untreated
Conclusion
Hydrocephalus is a serious neurological condition that can remarkably affect physical, cognitive, and functional abilities. Early medical intervention combined with structured physiotherapy rehabilitation is essential to enhance motor development, prevent complications, and promote independence. A multidisciplinary approach ensures optimal long-term outcome.
What is hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a condition caused by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, leading to increased intracranial pressure.
What are the common signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus?
Enlarged head size, headache, vomiting, delayed development, seizures, balance problems, and gait disturbances.
How does physiotherapy help in hydrocephalus management?
Physiotherapy improves mobility, balance, strength, motor development, and functional independence, especially after shunt surgery.