Introduction:
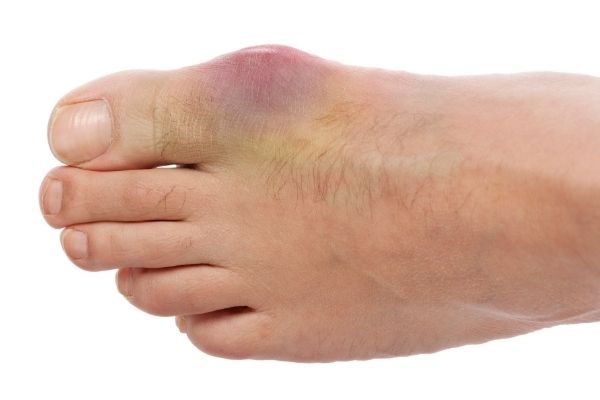
Gout is a disorder of purine metabolism characterized by hyperuricaemia, deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in joints and periarticular tissues, and recurrent attacks of synovitis.
Causes:
- Elevated Uric Acid Levels (Hyperuricemia): The primary cause is due to overproduction or decreased excretion of uric acid.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history increases susceptibility.
- Dietary Factors: High intake of purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, and alcohol.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Poor kidney function reduces uric acid elimination.
- Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle: contribute to metabolic imbalance and increased uric acid production.
- Chronic diseases: including hypertension, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, are common contributors.
Affected Area:
The common sites are the small joints of hands and feet, the metatarsophalangeal joints of the big toe, the ankle and fingers, and the olecranon bursae.
Signs and Symptoms:
Severe Joint Pain: Often begins at night or early morning.
Redness and Warmth: Inflammation causes the joint to appear red and hot.
Swelling: Rapid swelling around the affected joint.
Tenderness: Even a light touch may cause extreme pain.
Fever and Malaise: May accompany acute gout attacks.
Reduced Range of Motion: Pain and swelling limit joint mobility.
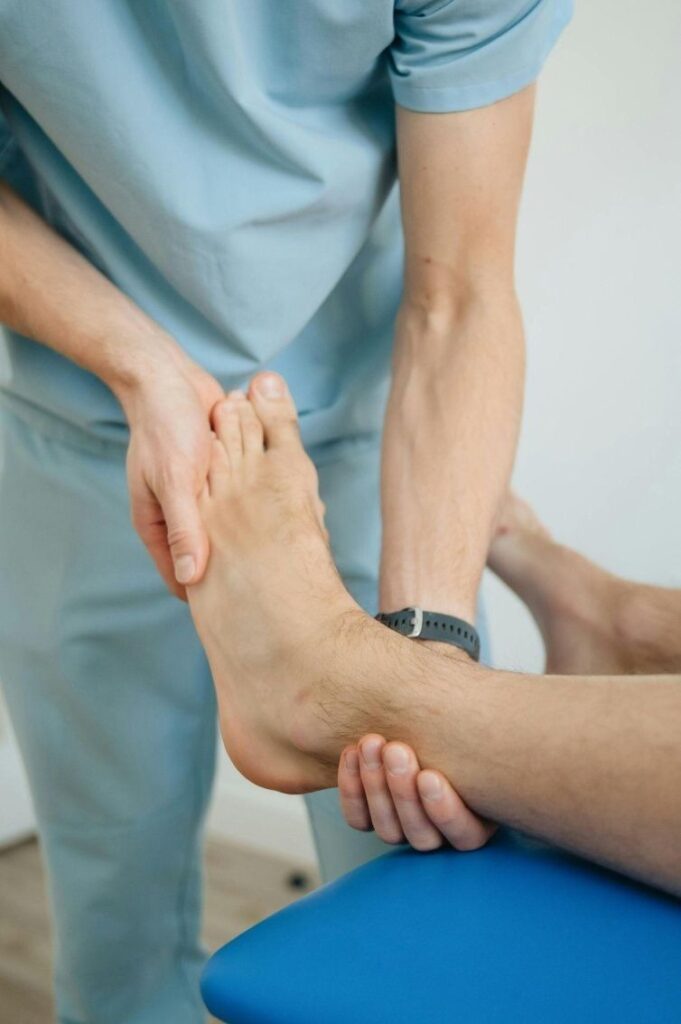
Physiotherapy Management:
Range of Motion Exercises: Maintain joint mobility once acute pain reduces.
Strengthening Exercises: For ankle and foot intrinsic strengthening after subsiding pain.
Gait Training: If lower limb joints are involved, proper walking patterns are toughened.
Weight Management Education: Guidance on safe exercises to reduce obesity-related strain.
Lifestyle Modification: Advice on diet, hydration, and reducing alcohol intake.
Conclusion:
Gout is a painful yet highly manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated appropriately. With proper medical care, lifestyle changes, healthy dietary habits, and physiotherapy support, individuals can protect joint function and upgrade overall quality of life. Consistent management is key to preventing long-term complications.
What is gout?
Answer: Gout is a metabolic disorder caused by high uric acid levels, leading to crystal deposits in joints and recurrent painful inflammation.
What are the common signs and symptoms of gout?
Answer: Severe joint pain, redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness, fever, and reduced joint movement.
How does physiotherapy help in gout management?
Answer: Physiotherapy improves mobility through range-of-motion and strengthening exercises, supports gait training, and guides lifestyle and weight management.