Introduction
Pleurectomy is a surgical procedure involving partial or complete removal of the pleura—the thin membrane lining the lungs and chest wall. It is commonly performed to control recurrent pleural conditions and improve lung expansion. Appropriate postoperative care and physiotherapy are necessary for optimal respiratory recovery.
procedure
Pleurectomy is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia to remove part or all of the pleura lining the chest cavity. After positioning the patient, the surgeon accesses the thoracic cavity through thoracotomy or video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). The diseased pleural tissue is carefully separated and excised from the lung surface and chest wall. Bleeding is controlled, and lung expansion is ensured. A chest tube is placed to drain air and fluid, and the incision is closed in layers. Postoperatively, pain control, chest physiotherapy, and monitoring are essential for recovery.
Indications
Pleurectomy is indicated in the following conditions:
- Recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax
- Chronic pleural effusion unresponsive to conservative treatment
- Recurrent pleural infections or empyema
- Malignant pleural diseases
- Persistent air leak from the lung
Contraindications
Pleurectomy may not be suitable in certain cases, including:
- Severe cardiopulmonary instability
- Inability to tolerate general anesthesia
- Poor general health or advanced frailty
- Extensive metastatic disease with limited life expectancy
- Severe coagulation disorders
- Uncontrolled infection or sepsis
Signs and Symptoms
Patients undergoing pleurectomy may experience:
- Chest pain at the surgical site
- Shortness of breath
- Reduced chest expansion
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shallow breathing due to pain
- Cough with or without sputum
- Decreased exercise tolerance
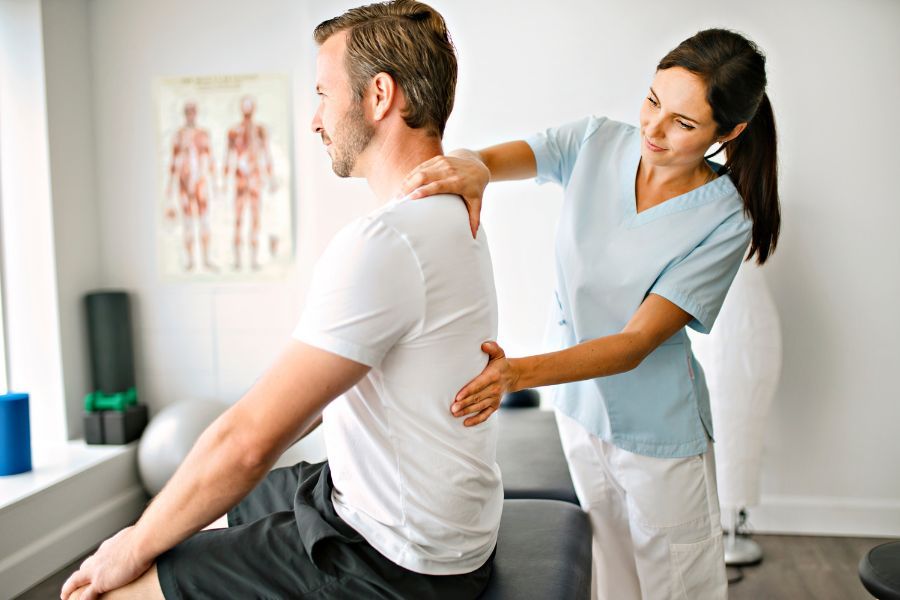
Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in recovery following pleurectomy:
- Breathing exercises to improve lung expansion
- Incentive spirometry to prevent atelectasis
- Postural drainage and airway clearance techniques, if required
- Chest mobility and thoracic expansion exercises to prevent lung complications
- Early mobilization to reduce complications
- Upper limb range of motion exercises to prevent shoulder stiffness
- Gradual endurance and functional training
- Patient education on breathing control and posture
Physiotherapy helps restore respiratory function, prevent pulmonary complications, and enhance overall quality of life.
Complications
Possible complications associated with pleurectomy include:
- Postoperative pain and stiffness
- Prolonged air leak
- Bleeding or hemothorax
- Infection
- Reduced lung compliance
- Respiratory complications such as pneumonia
- Shoulder dysfunction due to thoracic surgery
Conclusion
Pleurectomy is an effective surgical intervention for managing recurrent and chronic pleural disorders. While it can remarkably improve lung function and symptom control, comprehensive postoperative physiotherapy is essential for optimal recovery. A multidisciplinary approach ensures decreased complications, improved respiratory efficiency, and better functional outcomes.
Q1. What is pleurectomy and why is it performed?
Pleurectomy is the surgical removal of part or all of the pleura to manage recurrent pleural disorders and improve lung expansion.
Q2. What are the common indications for pleurectomy?
It is indicated in recurrent pneumothorax, chronic pleural effusion, pleural infections, malignant pleural disease, and persistent air leaks.
Q3. What is the role of physiotherapy after pleurectomy?
Physiotherapy improves lung expansion, prevents respiratory complications, restores chest mobility, and enhances functional recovery.