Introduction
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a commonly performed cardiac surgical procedure used to restore adequate blood flow to the heart muscle. It is recommended for patients with severe coronary artery disease (CAD) where blood supply to the myocardium is remarkably decreased. CABG improves survival, relieves symptoms, and enhances quality of life.
Indications
CABG is indicated in patients with:
- Severe multi-vessel coronary artery disease
- Significant blockage not suitable for angioplasty
- Left main coronary artery stenosis
- Recurrent angina despite optimal medical management
- Reduced left ventricular function with ischemia
- Failed or restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
Contraindications
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting may be relatively or absolutely contraindicated in:
- Advanced multisystem organ failure
- Severe uncontrolled infection
- Severe pulmonary disease with high operative risk
- Limited life expectancy due to non-cardiac illness
- Diffuse coronary disease is unsuitable for grafting
Signs and Symptoms
Patients requiring CABG often present with:
- Chest pain or angina
- Fatigue and decreased exercise tolerance
- Shortness of breath on exertion
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
- Symptoms of heart failure in advanced cases
Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in both pre- and post-operative rehabilitation:
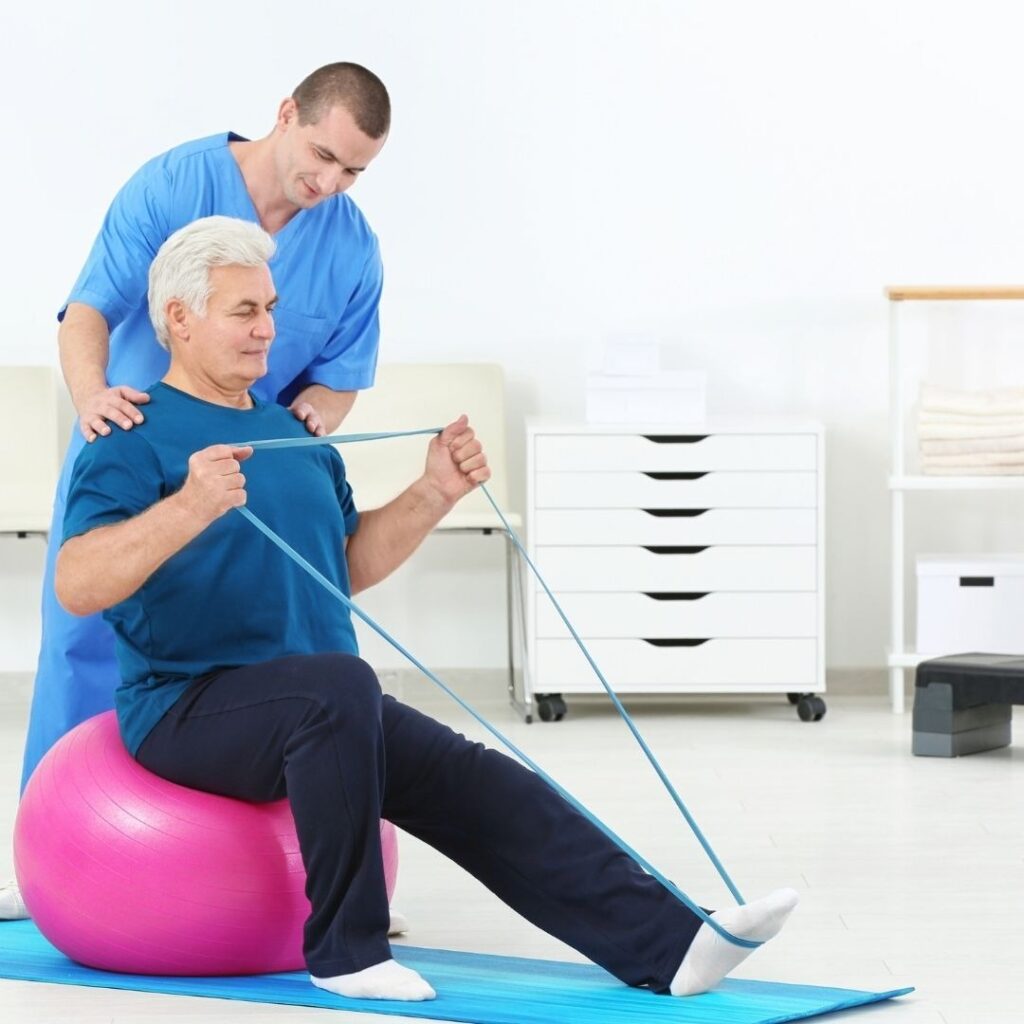

Preoperative Phase
- Breathing exercises to improve lung capacity
- Patient education on post-surgical care
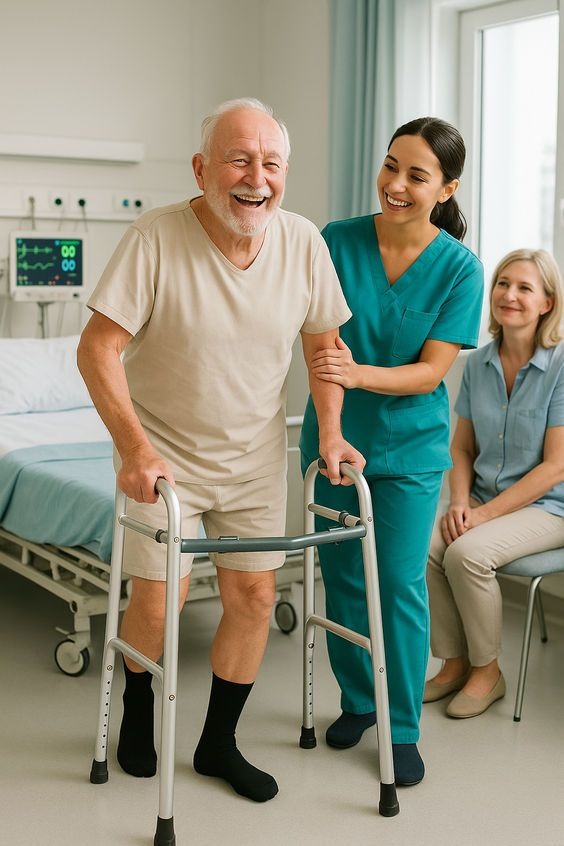

Postoperative Phase
- Chest physiotherapy to prevent pulmonary complications
- Deep breathing and incentive spirometry
- Early mobilization and ambulation
- Upper limb and trunk mobility exercises
- Gradual aerobic conditioning
- Postural correction and sternal precautions education
Physiotherapy helps improve cardiopulmonary function, reduce complications, and accelerate recovery.
Complications
Possible complications of CABG include:
- Wound infection
- Arrhythmias (especially atrial fibrillation)
- Myocardial infarction
- Atelectasis and pneumonia
- Stroke
- Sternal instability
- Reduced functional capacity if rehabilitation is delayed
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting is a life-saving surgical intervention for patients with advanced coronary artery disease. With appropriate patient selection, skilled surgical care, and structured physiotherapy rehabilitation, CABG remarkably improves cardiac function, functional independence, and long-term outcomes. Early mobilization and rehabilitation are essential for optimal recovery.
Q1. What is Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)?
A: CABG is a cardiac surgery that restores blood flow to the heart muscle in patients with severe coronary artery disease.
Q2. When is CABG indicated?
A: It is indicated in multi-vessel coronary disease, left main artery stenosis, or recurrent angina despite medical treatment.
Q3. What is the role of physiotherapy after CABG?
A: Physiotherapy improves lung function, promotes early mobilization, prevents complications, and accelerates functional recovery.